Photo: Edgewater Medical Center looms over the bustling neighborhood.
When an animal in the wild suffers from some genetic or incidental malady the results are often fatal. Years of natural selection from generation to generation insure that only those who are best suited to survive in their environments will continue to survive. One of the things that sets humans apart from animals is that we make every effort to insure that our species will continue to thrive in spite of what ails our bodies. Medical staff are ethically obligated to provide the best possible quality of care for patients, no matter the affliction. For some executives and doctors at Chicago’s Edgewater Medical Center personal profits came before those ethical standards, while they used the best hospital beds for this purpose. The unnecessary suffering and premature deaths they caused resulted in the shuttering of a historic Chicago neighborhood hospital. The tragedy makes one wonder if the culprits are even human at all.
Photo (Chicago History in Postcards): Edgewater Medical Center as it appeared in the 50-60s. The original building is to the left and Mazel House 1953 expansion to the right.
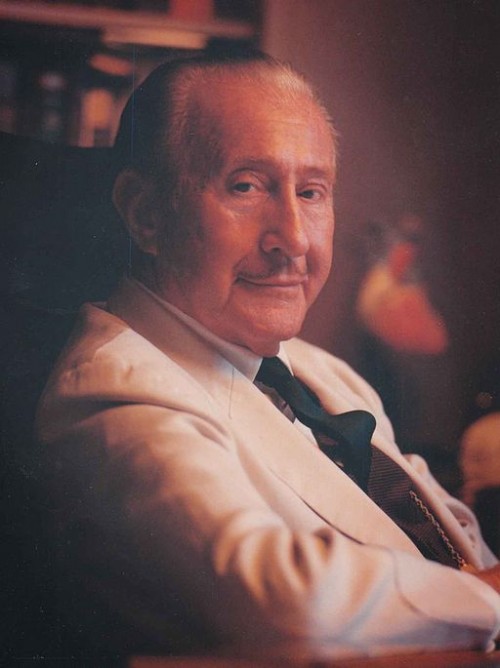
Dr. Maurice Mazel founded the Edgewater Hospital at the outset of the Great Depression in 1929. He personally oversaw hospital operations until his death in 1980. During his tenure notable births included current US Secretary of State Hillary Rodham Clinton and serial killer John Wayne Gacy. His wife, Circus Hall of Fame performer Harriet Mazel-Szanto, functioned as chairman and CEO from 1980 to 1984. She later shed the CEO title, but remained on as chairman until 1988. After her passing the hospital built under the benevolent Mazel family name sought new ownership.
Photo (Wikimedia Commons): The benevolent Dr. Maurice Mazel reclining for his photograph.
Businessman Peter Rogan acquired Edgewater Medical Center in 1989 for $1 million cash and assumed its $10 million in liabilities through the Edgewater Operating Company (EOC) he created. In 1994 Rogan sold EOC and the real estate to the Edgewater Property Company (EPC), which he also controlled. In the deal Edgewater Medical Center paid an exhorbitant $79,500/mo. rent to EPC. At the helm of both entities Rogan funneled profits directly into his own pockets.
Corruption rooted itself deep into Edgewater’s staff. Rogan orchestrated a complex system of kickbacks for doctors and staff complicit with committing fraud against Medicare, Medicaid and private insurance companies. Vice president Roger Ehmen and medical director Dr. Ravi Barnabas were able to turn the nearly bankrupt hospital into a lucrative profit center. The pair tapped Dr. Sheshiqiri Rao Vavilikolanu and Dr. Kumar Kaliana to recruit potential patients. For years the doctors sent hospital employees into the Chicago community to find potential patients. It did not matter if they did not have heart conditions, were drug addicts, were unable to speak English or even had no health insurance coverage. Recruiters instructed the potential patients how to feign symptoms in order to mandate services rendered by Edgewater Medical Center. In return the patients were offered money, food, cigarettes and other amenities for their cooperation.
Another complicit Edgewater physician participated in the massive fraud scheme. Dr. Andrew Cubbria tapped into the recruited patient pool for unnecessary angiogram and angioplasty operations. Albert Okaro, 42, underwent an invasive and unnecessary cardiac surgery that ultimately killed him. The patient’s death was regarded as collateral damage for Dr. Cubria. Tax-payer funded healthcare programs and private insurers reimbursed the hospital for more than 750 invasive, and expensive, cardiac surgeries performed by Dr. Cubria alone.
One Edgewater physician, Dr. Krishnaswami Sriram, billed the government for seemingly impossible human feats. According to Dr. Sriram’s billing records on November 12, 1997 he saw 187 patients… all of whom coincidently had congestive heart failure. In January 1999 a severe snowstorm brought Chicago to a standstill. Despite the hazardous weather conditions Dr. Sriram was apparently able to visit 31 elderly patients at their homes and 18 more in medical facilities. Thirty-two of Dr. Sriram’s patients also managed to incur new medical costs long after their deaths. On paper it appeared as though Dr. Sriram was indefatigable. His records indicate that he met with patients every single day in 1997 and 1998, while missing only two days of work in 1999.
Photo: Collected tissue sample slides filed away.
Dr. Sriram’s apparent superhuman ability to visit patients did not go by unnoticed. Some of the elderly patients he targeted began to grow suspicious after noticing over-inflated billings on Explanation of Benefit forms. At least 15 patients contacted the Wisconsin Physicians Service, which handles claims in the Illinois area. Wisconsin Physicians Service alerted the FBI and they immediately began an investigation.
Things began to unravel in 1999 when the hospital payed out over $1 million to stave off an impending federal lawsuit over Medicare billing irregularities. The ambitious Dr. Sriram was taken into custody in 2000. Feds exposed the rest of the fraud operation in 2001.
The upheaval brought on by the charges cut the hospital’s day-to-day operations off at the knees. In November 2001 the US government, which accounted for 90% of Edgewater Medical Center income, ceased Medicare payments indefinitely. Unable to find a suitable financier the hospital shut down in December 2001. The remaining 450 staff were suddenly out of a job or had to transfer to other area healthcare facilities. In addition to the displaced staff, 52 patients were transferred to other facilities for ongoing care.
Photo: Patient records stacked on the floor almost reach the ceiling.
In 2006 courts ruled that former owner and executive Peter Rogan was on the hook for $64.2 million in damages and penalties. The US Justice Department charged Rogan in 2008 with obstruction of justice and perjury for his attempts to hide his assets. One of the trusts was set up in the Bahamas and was entitled the Peter Rogan Irrevocable Trust. Rogan insisted that he maintained no control whatsoever over the assets and could not access it. In addition to the federal charges, French bank Dexia is working with the Justice Department to recover assets scattered throughout various bank accounts and front companies in the Caribbean. The cases are still in litigation.
Senior vice president Roger Ehmen and Dr. Ravi Barnabas were convicted for their roles in the fraud operation. Ehmen received 6 1/2 years of prison time and was ordered to pay $5 million in restitution. Ehmen was quoted at sentencing stating,”Words alone cannot describe the deep sorrow and regret I have. I will have to live with this guilt for the rest of my life.” Medical director Dr. Barnabas was sentenced to 4 years and 4 months prison time and ordered to pay $1.1 million in restitution. Dr. Barnabas’ physician license is still listed as active in Illinois.
Photo: A photo of the human heart with arteries highlighted.
Dr. Sheshiqiri Rao Vavilikolanu confessed that he unnecessarily admitted over 900 patients. He was sentenced to 3 years and 11 months prison time and ordered to repay $6 million to Medicare and Medicaid. Dr. Vavilikolanu’s license is listed as suspended. Dr. Kumar Kaliana admitted to mail and healthcare fraud. He received a 1 year and 4 months sentence and forced to return $156,000, along with $1.1 million in restitution. Dr. Kaliana’s physician license is still listed as active.
The courts came down most heavily upon Dr. Andrew Cubria. In addition to Albert Okaro’s untimely death in 2000, the feds discovered that at least one more unnecessary cardiac operation resulted in the death of another patient in 1999. Dr. Cubria was sentenced to 12 1/2 years prison time for his wrongdoing. He was also ordered to return $2 million of his profits and pay $14.4 million in restitution. His physician license was suspended thereafter.
The man whose superhuman feats caught the eyes of the FBI was also brought to justice. A teary-eyed Dr. Sriram wept as he plead guilty to mail fraud, healthcare and tax fraud. He faces up to 18 years in prison, but he has been appealing that ruling. As part of his plea the doctor has agreed not to practice medicine and his physician license is listed as on probation in Illinois.
Photo: A massive x-ray machine still residing within the hospital.
After a decade of abandonment Edgewater residents are aiming to rid themselves of the abandoned hospital. According to The New York Times the property is in the hands of the Edgewater Medical Center Bankruptcy Estate, which is comprised of 250 creditors who are still owed in excess of $110 million. Of the creditors French bank Dexia is owed in excess of $55 million. Unable to recoup their costs creditors would like to see the hospital razed in favor of a business development. Edgewater community members would rather have the real estate transformed into park land. According to an official city-authorized assessment the hospital is valued at $5.9 million. The cost to demolish the hospital is estimated to be $6.5 million alone.
What will happen to that hollowed-out shell that was once Edgewater Medical Center? With the American economy on track for an extended downturn it is unlikely that private developers will invest in the property. With federal, state and city budgets already slim it is unlikely that a public works project will be in the pipeline anytime soon.
Photo: One of the intensive care units in the abandoned hospital.
A healthy portion of large abandoned buildings that urban explorers seek out are left behind after major changes in economic markets, competition and innovation leave stagnant companies behind. That is not the case with Edgewater Medical Center. What sets this building apart from other urbex locations is that it was created by criminal acts over an extended period of time. Even though the hospital was dated, they were still operating in a capacity that for the most part benefitted patients. By the time the FBI discovered the corruption it had already metastasized and killed Edgewater Medical Center.
Like most hospitals with chronologically staggered additions it is a winding labyrinth. Some of the floors look practically identical and it is easy to lose ones bearings. Yet each section of the hospital is still unique in its own way. Biohazard containers, alcohol swabs, diabetic supplies and other pharmaceutical supplies are littered throughout some of the rooms. Medical records, tissue samples, autopsy records and medical images can still be found in one of the labs. Heavy equipment such as a hyperbaric chamber and x-ray machine are tucked away behind closed doors. Above the Kadin Memorial Nurses’ Residence is an filthy empty pool under a skylight. Vintage furniture from the 1970’s occupies some of the rooms even though eviction notices from 2002 are matted into the floor. The administration building is, perhaps poetically, completely devoid of and vibrant momentos of life. It is quite unsettling to see a once intentionally sterile hospital environment ravaged by the uninhibited destructive elements of nature.
Photo: Vintage furniture still occupies some of the nurses’ apartments.
The story of Edgewater Medical Center foreshadowed many of the problems that plague the American healthcare industry today. Profit-focused healthcare endangered the lives of those who could not or were unable protect themselves. Patients at Edgewater Medical Center were exploited by the greed of administrators and doctors to the tune of millions. The system failed and took vital healthcare services away from one Chicago neighborhood.
The United States is and remains the only industrialized nation to not offer all citizens access to public healthcare options. There are now over 50 million Americans without health insurance of any kind. Even those fortunate enough to be insured are at the mercy of a healthcare system driven entirely by profit motives. Health decisions are prioritized every day to keep businesses in the black, rather than keep patients living long and healthy lives.
Photo: One of the laboratories with numerous patient records and equipment.
Resources:
Flickr – My photoset of the abandoned hospital.
BNet – Mentions Edgewater Hospital founder Dr. Mazel.
Chicago History in Postcards – Old postcard of Edgewater Medical Center.
Chicago News Cooperative – 2010 article on the abandoned hospital.
Chicago Tribune – 1989 article marking Harriet Mazel-Szanto’s death at Edgewater Medical Center.
Chicago Tribune – 1999 article on Edgewater staff paying out to avoid Medicare fraud litigation.
Chicago Tribune – 1999 article discussing AARP research on for-profit hospitals.
Chicago Tribune – 2000 article on Edgewater Dr. Sriram’s billing of dead patients.
Chicago Tribune – 2001 article about Edgewater closing its doors.
Chicago Tribune – 2001 article on Roger Ehmen’s and Dr. Ravi Barnabas’ sentencing.
Chicago Tribune – 2001 article on sentencing for Dr. Sheshiqiri Rao Vavilikolanu and Dr. Kumar Kaliana.
Chicago Tribune – 2001 article on convictions related to the Edgewater fraud case.
Chicago Tribune – 2002 article on Dr. Cubria’s sentencing.
Chicago Tribune – 2002 article on Dr. Sriram’s sentencing.
Chicago Tribune – 2004 article outlining settlement from Albert Okaro’s death.
Chicago Tribune – 2008 article on the case against former chief executive Peter Rogan.
Chicago Tribune – 2009 article detailing the recovery of Peter Rogan’s assets.
Chicago Tribune – 2010 article on the hospital’s future. Land Value: $5.3m. Demo: $6.5m estimated.
Christopher T. Hurley & Associates Newsletter – Dr. Andrew Cubria specifically selected poor and Spanish speaking patients to commit fraud.
Coalition Against Insurance Fraud – 2002 blog on Dr. Andrew Cubria, who performed 750 unnecessary invasive procedures.
Curbed Chicago – Plans for redevelopment into a park with pictures.
Edgewater Historical Society – Small entry on Edgewater Medical Center.
Facebook – Group for people born at Edgewater Medical Center.
Flickr – Comptesse DeSpair’s great set of Edgewater Medical Center photos.
Flickr – Search for “Edgewater Hospital” ranked by interestingness.
Google – Search for Edgewater Medical Center 1970-2011.
Hospital Data – Statistics for Edgewater Medical Center.
The New York Times – Examines economic difficulties for redevelopment.
NWI – 2008 article on the international battle over recovering Peter Rogan’s assets.
US Bankruptcy Court – 2007 bankruptcy court ruling against Braddock Management and Bainbridge Management.
US Department of Justice – 2003 press release for criminal fraud charges and $2.9 million civil judgement against the management firms that ran Edgewater.
US Department of Justice – 2008 press release detailing charges against owner Peter Rogan.
QuoteUs – Insurance blog article on the most outrageous insurance frauds. Mentions Edgewater doctor Andrew Cubria.
Yahoo – Recent efforts by Edgewater residents to turn the complex into a park.
Wikipedia – US Secretary of State Hillary Rodham Clinton was born at Edgewater Medical Center.
Wikipedia – Convicted serial killer John Wayne Gacy was born at Edgewater Medical Center.